Parting away with your hard-earned money is not easy and especially when a huge chunk of the income goes away as taxes every year. With the tax season around, saving up on taxes is topmost priority for everyone who is liable to pay taxes. There are many options under the Income Tax Act which help you to lower your tax liability and if utilised fully they can reduce your tax outgo by a considerable amount.
Two such options which help you lower tax liability are tax exemptions and tax deductions. Very often people consider them to be one and the same thing and use these two words interchangeably. Though they both serve the same objective of lowering your taxes but in reality tax exemption and tax deduction are different provisions of the Income Tax Act. Thus, it is extremely crucial to understand the difference between the two in order to utilise these provisions correctly to lower your tax liability.
What is tax exemption?
Exemption is basically a reduction from the income related to a particular head of income for and can be claimed from the particular head of income only. Income from a specific head is calculated after deducting the exemptions and such then the income from different heads is added to arrive at the gross total income. Thus, exemptions are excluded from the gross total income of an individual. Depending upon the type of income they may be completely or partially exempt from tax.
Here are a few important exemptions that make a part of your salary tax-free.
House & Rent Allowance
If you receive HRA as a component of your salary it is deductible from your gross salary for income tax computation to the lowest of the following:
- Actual HRA received
- 50% of [Basic salary + DA] for those living in metro cities (40% for non-metros)
- Actual rent paid less 10% of salary
Conveyance Allowance:
The component in your salary allocated as ‘conveyance allowance’ is actually exempt from taxation. Any allowance you receive as conveyance allowance is tax-free to the extent of INR 19,200 annually.
Professional Tax
In most cases you would notice a couple of hundreds being deducted towards ‘professional tax’ each month- this typically adds up to INR 2,500 annually. This is a tax levied by states and the maximum amount that can be levied is INR 2,500. You can actually reduce this amount from your gross income while computing taxes – this tax is an exempt component.
What is tax deduction?
Deduction, on the other hand, is the reduction in the gross total income of the taxpayer for investments made or expenditures incurred for specific financial instruments specified by Section 80 of the Income Tax Act. Tax deductions were basically introduced to incentivise and encourage investors to start saving and investing for long-term financial goals. For example,
Here are a few deductions that will help you lower your tax burden and add value to your financial position as well.
Section 80C – deductible investments
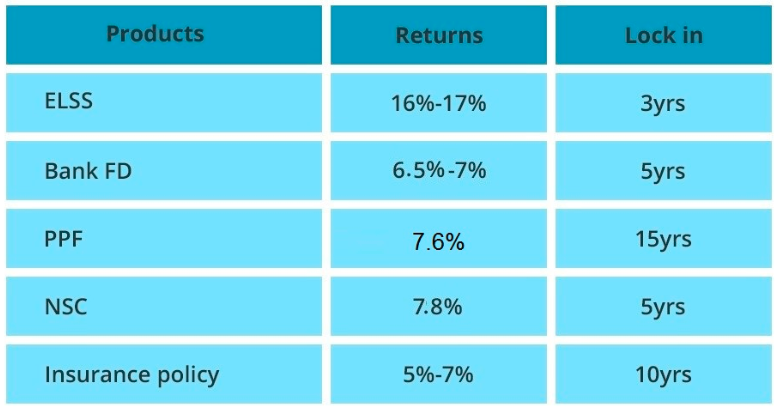
Section 80C allows certain investments to be deducted from the gross total income before computing income tax incidence to an extent of INR 1.5 lakh. Typically, these products have a lock-in period and the returns varies across products.
Following is a typical snapshot of the options available.
Section 80D
Health insurance premia paid for you, your spouse or dependent children are deductible to the extent of INR 25,000. Premia paid towards a health insurance for your parents allows for an additional INR 25,000 as a deduction and goes up to INR 30,000 if your parents are above 60 years of age.
Section 80E – Education Loan
If you’ve availed an education loan, all the interest you pay on the loan is deductible under section 80E. There’s no maximum limit to the amount; however, you can avail this deduction only for eight years of payment starting from the year in which the repayment begins.
Let us look at the comparison between tax exemption and tax deduction to fully understand the two concepts:
| Key difference | Tax Exemption | Tax Deduction |
| Meaning | Exemptions are exclusions in the income therefore they are not included in the taxable income. In order to arrive at the gross taxable income such exemptions are excluded beforehand. | Deductions are a part of the taxable income. After the gross total income is calculated then the deductions are subtracted from it to arrive at the net taxable income. |
| Application | Exemptions are applicable to a particular head of income and can be claimed from that head only. It cannot be claimed from gross taxable income. | Deductions are applicable only on the gross total income and not from any specific head of income. |
| Importance | Tax exemptions are essentially incomes which are excused from the payment of taxes either fully or partially. | Tax deductions are those investments and expenditures which are liable for payment of taxes but because of the provisions of the act, they can be claimed as deductions resulting in reduction of the income. |
Thus, both tax exemptions and tax deductions serve the same purpose of lowering your tax outgo but they are two different things and in order to make the most of these provisions you must fully understand the difference in order to file your returns properly.



























